Throttle Follower
Throttle Follower Target
Axis selection and changing values
This table is intended to be used with RPM set as the first/x (left to right) axis and Pedal Position Source as the second/y (bottom to top) axis, though these axes are user configurable to use any ECU channel. Changing the axis values can be accomplished by pressing F3 when the table is selected, then either editing an existing value or adding a new value. Note that if you edit an axis site value, the overall table values will be adjusted so that the shape of the table is unchanged.
Tuning
Only available when the Throttle Follower is enabled. This is the target for the Throttle Follower Idle Offset. This table is always active whenever the Throttle Follower is enabled. For this reason, when pedal position is 0 around idle conditions, table values must be 0 (at higher RPM and 0 values for pedal position, the target can be positive, however must be low as to ensure correct return to idle). The Throttle Follower Target is typically mapped to have a larger amount when either rpm or load is increased - these sites must be tuned by feel. This can be done on a dynamometer, however road testing is suggested to ensure correct feel.For a vehicle equipped with a DBW Throttle, the Throttle Follower Target % is a percentage of the DBW Max Position setting. Note that if Idle Control is demanding close to the max position, the Throttle Follower Target offset will not allow the throttle position to exceed the set Max Throttle Position.Note that the decay time is used whenever the value is decreasing; typically when closing throttle.
Throttle Follower Decay
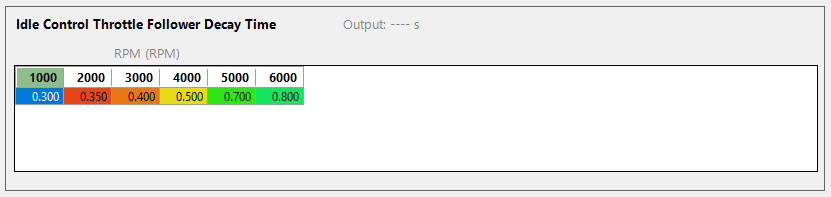 Only available when the Throttle Follower is enabled. This controls the amount of time to decay the Throttle Follower Target away. This decay is started when the throttle is moving in the closed direction. Traces below show this in action.
Only available when the Throttle Follower is enabled. This controls the amount of time to decay the Throttle Follower Target away. This decay is started when the throttle is moving in the closed direction. Traces below show this in action.
DBW Vehicles
The white circle shows where the Throttle Follower decay is active. The throttle follower output and target are the same as the throttle is increased, however when the throttle is closing, the decay table is active, causing the Throttle Follower output to decay over a set time.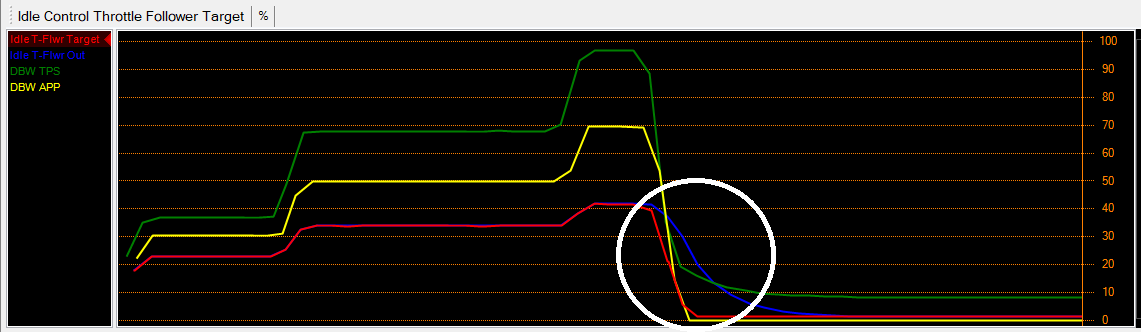 This in turn slows the rate of closing of the throttle (for DBW vehicles only, as the idle control is output by the DBW throttle). This is seen where the throttle position (green trace) decays slowly in comparison to the accelerator pedal position (yellow trace). This is shown more clearly in the trace below.
This in turn slows the rate of closing of the throttle (for DBW vehicles only, as the idle control is output by the DBW throttle). This is seen where the throttle position (green trace) decays slowly in comparison to the accelerator pedal position (yellow trace). This is shown more clearly in the trace below.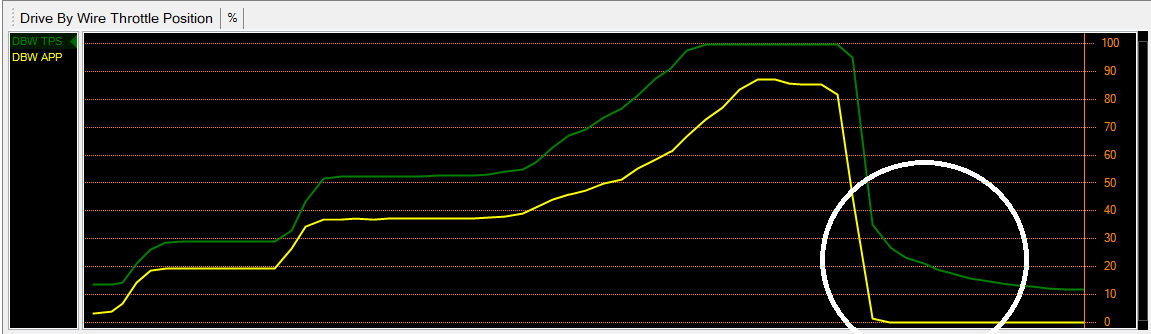
Non-DBW Vehicles
The white circle shows where the Throttle Follower decay is active. The throttle follower output and target are the same as the throttle is increased, however when the throttle is closing, the decay table is active, causing the Throttle Follower output to decay over a set time.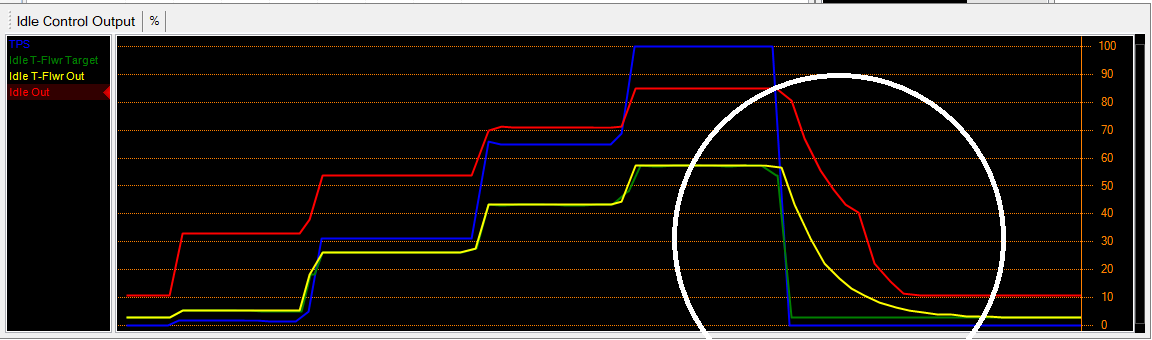 This in turn slowly returns the idle control offset back to normal idle conditions, as seen where the Idle Control Output (red trace) decays slowly in comparison to the throttle position (blue trace). The trace below shows the Throttle Follower output decay compared to the throttle position.
This in turn slowly returns the idle control offset back to normal idle conditions, as seen where the Idle Control Output (red trace) decays slowly in comparison to the throttle position (blue trace). The trace below shows the Throttle Follower output decay compared to the throttle position.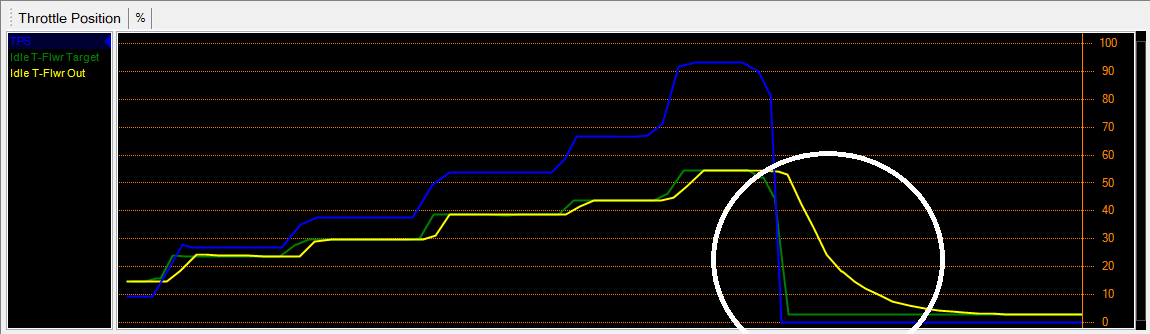
Related Articles
Idle Control
Idle Control The Idle Control function allows your ECU to control the engine idle speed. There are multiple ways this is achieved with either Drive-By-Wire (DBW) control, a Bypass Air Control (BAC) solenoid with either two or 3 wire types, or via a ...Idle Control
The Idle Control function allows your Elite ECU to control the engine idle speed. There are multiple ways this is achieved with either Drive-By-Wire (DBW) control, a Bypass Air Control (BAC) solenoid with either two or 3 wire types, or via a Stepper ...Idle Control Tuning
Idle Control is used to hold the RPM steady while off the throttle. To do this the ECU needs to be controlling a device that regulates air flow into the engine. This can be via DBW throttle control, a 2 or 3 wire solenoid, or a stepper motor valve. ...Idle Control Wiring
This article explains the most common types of idle air control valves and how to wire them up using a Haltech Nexus or Elite ECU: Bypass Air Control (BAC) Two Wire This type of idle valve is the simplest to wire up, being a solenoid with just two ...Tuning for Idle (fuel)
The idle mixture is very sensitive to changes in injection time. Idle injection times are usually around 1.5 to 2.5 ms. If the injection time at idle is much lower than this, it may become difficult to set accurate idle and cruise air/fuel ratios. ...